
Using Google Maps in Android

POSTED BY WEIMENGLEE - 06 APR 2009
Google Maps is one of the many applications bundled with the Android platform. In addition to simply using the Maps application, you can also embed it into your own applications and make it do some very cool things. In this article, I will show you how to use Google Maps in your Android applications and how to programmatically perform the following:
- Change the views of Google Maps
- Obtain the latitude and longitude of locations in Google Maps
- Perform geocoding and reverse geocoding
- Add markers to Google Maps
(Note: we cover Google Maps API v2 here.)
Creating the Project
Using Eclipse, create a new Android project and name GoogleMaps as shown in Figure 1.
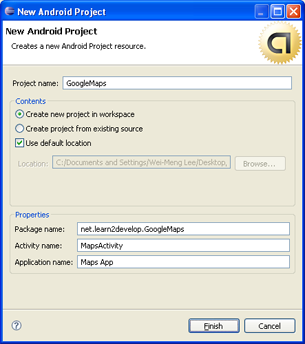
Figure 1 Creating a new Android project using Eclipse
Obtaining a Maps API key
Beginning with the Android SDK release v1.0, you need to apply for a free Google Maps API key before you can integrate Google Maps into your Android application. To apply for a key, you need to follow the series of steps outlined below. You can also refer to Google's detailed documentation on the process athttp://code.google.com/android/toolbox/apis/mapkey.html.
First, if you are testing the application on the Android emulator, locate the SDK debug certificate located in the default folder of
"C:\Documents and Settings\\Local Settings\Application Data\Android" . The filename of the debug keystore is debug.keystore. For deploying to a real Android device, substitute the debug.keystore file with your own keystore file. In a future article I will discuss how you can generate your own keystore file.
For simplicity, copy this file (
debug.keystore) to a folder in C:\ (for example, create a folder called "C:\Android").
Using the debug keystore, you need to extract its MD5 fingerprint using the
Keytool.exe application included with your JDK installation. This fingerprint is needed to apply for the free Google Maps key. You can usually find the Keytool.exefrom the "C:\Program Files\Java\\bin " folder.
Issue the following command (see also Figure 2) to extract the MD5 fingerprint.
Copy the MD5 certificate fingerprint and navigate your web browser to: http://code.google.com/android/maps-api-signup.html. Follow the instructions on the page to complete the application and obtain the Google Maps key.
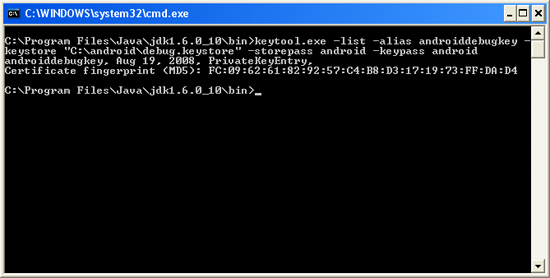
Figure 2 Obtaining the MD5 fingerprint of the debug keystore
To use the Google Maps in your Android application, you need to modify your
AndroidManifest.xml file by adding theINTERNET permission:Displaying the Map
To display the Google Maps in your Android application, modify the
main.xml file located in the res/layout folder. You shall use the
Notice from above that I have used the Google Maps key that I obtained earlier and put it into the
apiKey attribute.
In the
MapsActivity.java file, modify the class to extend from the MapActivity class, instead of the normal Activityclass:
Observe that if your class extends the
MapActivity class, you need to override the isRouteDisplayed() method. You can simply do so by setting the method to return false.
That's it! That's all you need to do to display the Google Maps in your application. Press
F11 in Eclipse to deploy the application onto an Android emulator. Figure 3 shows the Google map in all its glory.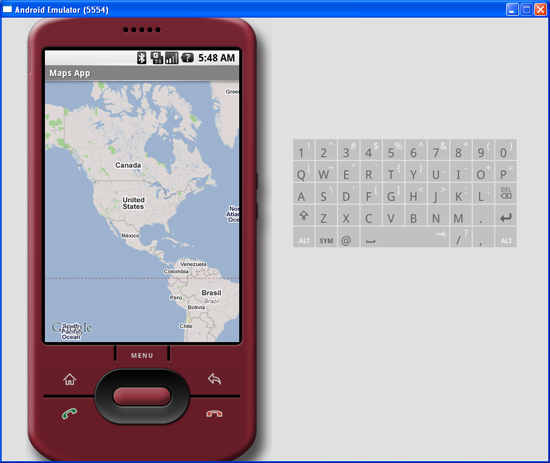
Figure 3 Google Maps in your application
At this juncture, take note of a few troubleshooting details. If your program does not run (i.e. it crashes), then it is likely you forgot to put the following statement in your
AndroidManifest.xml file:
If your application manages to load but you cannot see the map (all you see is a grid), then it is very likely you do not have a valid Map key, or that you did not specify the
INTERNET permission:Displaying the Zoom View
The previous section showed how you can display the Google Maps in your Android device. You can drag the map to any desired location and it will be updated on the fly. However, observe that there is no way to zoom in or out from a particular location. Thus, in this section, you will learn how you can let users zoom into or out of the map.
First, add a
main.xml file as shown below:
You will use the
In the
MapsActivity.java file, add the following imports:
and add the following code after the line
setContentView(R.layout.main);
The complete
MapsActivity.java file is given below:
Basically, you obtain the
MapView instance on the activity, obtain its zoom controls and then add it to the LinearLayoutelement you added to the activity earlier on. In the above case, the zoom control will be displayed at the bottom of the screen. When you now press F11 in Eclipse, you will see the zoom controls when you touch the map (see Figure 4).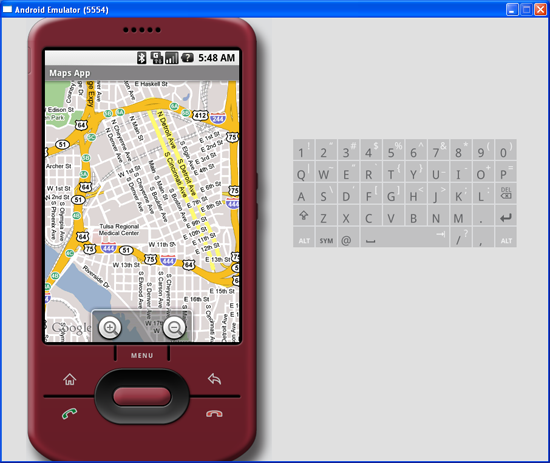
Figure 4 Using the zoom controls in Google Maps
Using the zoom control, you can zoom in or out of a location by simply touching the "+ or "-" buttons on the screen.
Alternatively, you can also programmatically zoom in or out of the map using the
zoomIn() and zoomOut() methods from the MapController class:
In the above code, when the user presses the number 3 on the keyboard the map will zoom in into the next level. Pressing number 1 will zoom out one level.
Changing Views of the Map
By default, the Google Maps displays in the map mode. If you wish to display the map in satellite view, you can use the
setSatellite() method of the MapView class, like this:
You can also display the map in street view, using the
setStreetView() method:
Figure 5 shows the Google Maps displayed in satellite and street views, respectively.
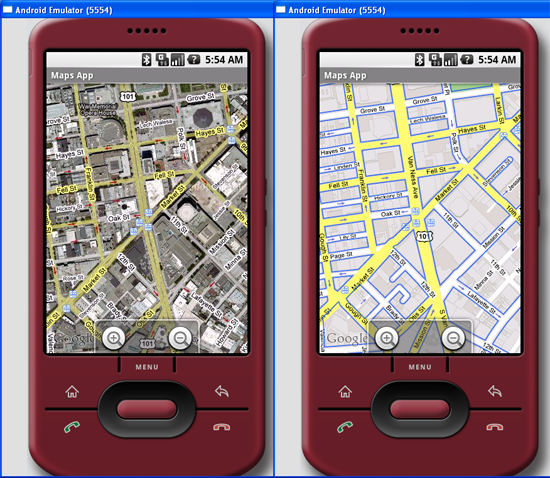
Figure 5 Displaying Google Maps in satellite and street views
Displaying a Particular Location
Be default, the Google Maps displays the map of the United States when it is first loaded. However, you can also set the Google Maps to display a particular location. In this case, you can use the
animateTo() method of theMapController class.
The following code shows how this is done:
In the above code, you first obtain a controller from the
MapView instance and assign it to a MapController object (mc). You use a GeoPoint object to represent a geographical location. Note that for this class the latitude and longitude of a location are represented in micro degrees. This means that they are stored as integer values. For a latitude value of 40.747778, you need to multiply it by 1e6 to obtain 40747778.
To navigate the map to a particular location, you can use the
animateTo() method of the MapController class (an instance which is obtained from the MapView object). The setZoom() method allows you to specify the zoom level in which the map is displayed. Figure 6 shows the Google Maps displaying the map of Singapore.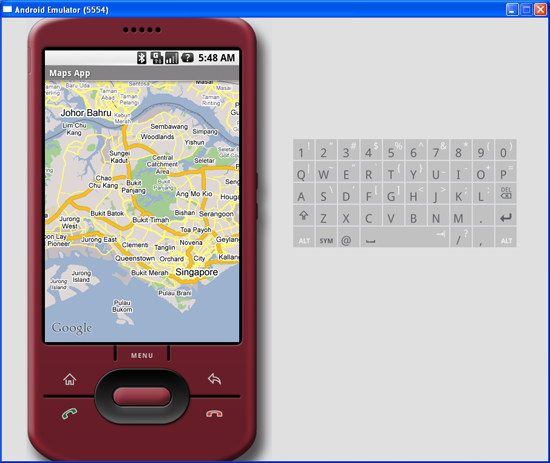
Figure 6 Navigating to a particular location on the map
Adding Markers
Very often, you may wish to add markers to the map to indicate places of interests. Let's see how you can do this in Android. First, create a GIF image containing a pushpin (see Figure 7) and copy it into the
res/drawable folder of the project. For best effect, you should make the background of the image transparent so that it does not block off parts of the map when the image is added to the map.
Figure 7 Adding an image to the res/drawable folder
To add a marker to the map, you first need to define a class that extends the
Overlay class:
In the
MapOverlay class that you have defined, override the draw() method so that you can draw the pushpin image on the map. In particular, note that you need to translate the geographical location (represented by a GeoPoint object, p) into screen coordinates.
As you want the pointed tip of the push pin to indicate the position of the location, you would need to deduct the height of the image (which is 50 pixels) from the y-coordinate of the point (see Figure 8) and draw the image at that location.
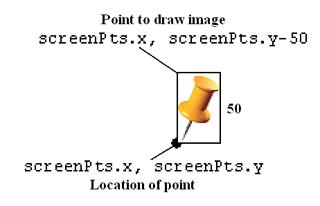
Figure 8 Adding an image to the map
To add the marker, create an instance of the
MapOverlap class and add it to the list of overlays available on the MapViewobject:
Figure 9 shows how the pushpin looks like when added to the map.
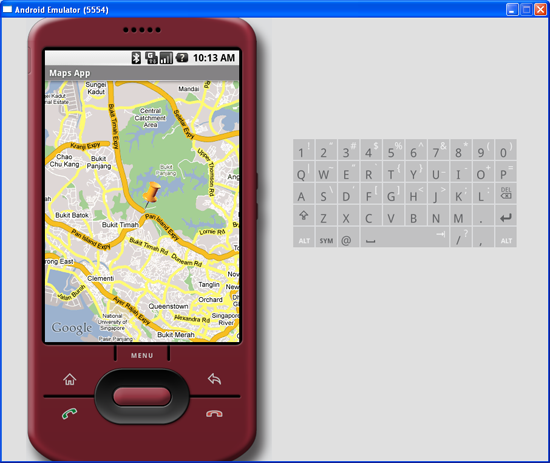
Figure 9 Adding a marker to the map
Getting the Location that was touched
After using Google Maps for a while, you may wish to know the latitude and longitude of a location corresponding to the position on the screen that you have just touched. Knowing this information is very useful as you can find out the address of a location, a process known as Geocoding (you will see how this is done in the next section).
If you have added an overlay to the map, you can override the onTouchEvent() method within the
Overlay class. This method is fired every time the user touches the map. This method has two parameters - MotionEvent and MapView. Using the MotionEvent parameter, you can know if the user has lifted his finger from the screen using the getAction()method. In the following code, if the user has touched and then lifted his finger, you will display the latitude and longitude of the location touched:
Figure 10 shows this in action.
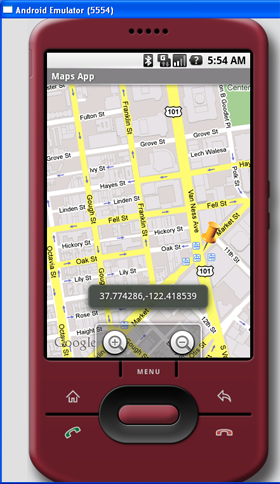
Figure 10 Displaying the latitude and longitude of a point touched on the map
Geocoding and Reverse Geocoding
If you know the latitude and longitude of a location, you can find out its address using a process known as Geocoding. Google Maps in Android supports this via the
Geocoder class. The following code shows how you can find out the address of a location you have just touched using the getFromLocation() method:
Figure 11 shows the above code in action.
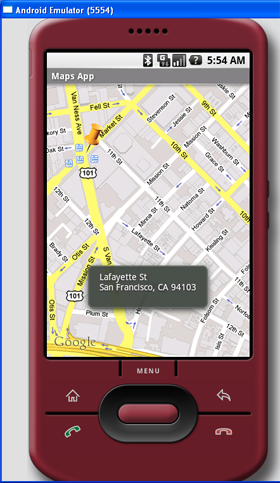
Figure 11 Performing Geocoding in Google Maps
If you know the address of a location but want to know its latitude and longitude, you can do so via reverse-Geocoding. Again, you can use the
Geocoder class for this purpose. The following code shows how you can find the exact location of the Empire State Building by using the getFromLocationName() method:
Once the location is found, the above code navigates the map to the location. Figure 12 shows the code in action.
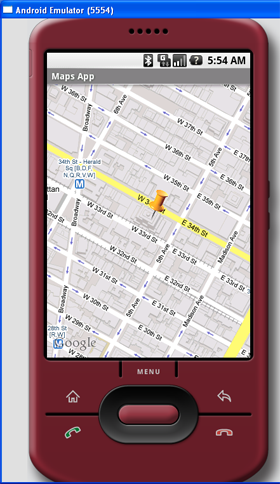
Figure 12 Navigating to the Empire State Building
Summary
In this article, you have learnt a few tricks for the Google Maps in Android. Using Google Maps, there are many interesting projects you can work on, such as geo-tagging, geo-tracking, etc. If you have cool ideas on building cool location-based services, share with us in the comments box below. Have fun!
Any ideas?
Here's my manifest:
POSTED BY AVDHESH 5 YEARS AGO
Hi,
Thanks for such a good article on maps. I found one issue in your block related to debug certificate on given locationC:\Documents and Settings\\Local Settings\Application Data\Android. When a generate the finger for specified location, after generating finger pint, i generate the api key. My app is running fine but i am not able to see any maps on emulator only grid view are there.
My problem is resolved when i get the debug key store on the given location:
C:\Documents and Settings\\.android\debug.keystore
C:\Documents and Settings\\.android\debug.keystore
Debug key store location on different operating systems.
➤ Windows Vista \users\\.android\debug.keystore
➤ Windows XP \Documents and Settings\\.android\debug.keystore
➤ Linux or Mac ∼/.android/debug.keystore
➤ Windows XP \Documents and Settings\\.android\debug.keystore
➤ Linux or Mac ∼/.android/debug.keystore
Hope this will help.
Thanks
Avdhesh
Avdhesh
POSTED BY CNBISHOP 5 YEARS AGO
thanks for a great tutorial! i was wondering, how can i add an additional marker to the spot when the user touches the map?
POSTED BY TRIPPLE60 5 YEARS AGO
Hello, I would like to use your great example on using google maps in android to learn and explore how the code works in eclipse with the JDK. Could you email me the source code on this so I can begin experimenting? Much appreciated.tripple60@gmail.com
Matt
POSTED BY GAURID3 5 YEARS AGO
Hi, I got the debug key for my application. I have added INTERNET permission too. The app loads but doesn't show the map in emulator. What can be the reason? Does it work behind proxy?
POSTED BY VIVEKASOHAN 5 YEARS AGO
good sample ya i got everything correctly
vivekasohanPOSTED BY LEON01061988 4 YEARS AGO
Hi ! i have got the same problem about the first time with the map did not show anything, except only grid. I have follow all those steps, about getting MD5 finger print, and Google Maps API key, also Internet permission.
Anyone who 's solved this problem before, please reply to me soon, thanks!
Anyone who 's solved this problem before, please reply to me soon, thanks!
Note: i have deployed on my own HTC phone (Wild Fire), may be there 's some different in set up environment or not ?
POSTED BY LEGEND 4 YEARS AGO
Great tutorial! Really appreciated for this great information for a newbee like me and it really helps!
POSTED BY KAMALONE 4 YEARS AGO
Hai ,
Thank you very much for the Great tutorial!! It Helped me a lot.
But i am getting error while modifying the code.
In my application has two xml file. One is first.xml and the other is main.xml
by starting first.xml is loading and it has viewMAP button. If click that going to main.xml and the map shows there.(It is showing correctly)
and the main.xml another buton is there for going back which allows the user to go back to first.XML(It is also working fine).
If i am again click the viewMAP button then the application shows "InfalteException:Binary xml file line #6: Error in inflating class ".
My Code is
POSTED BY DHRUVJOSHI 4 YEARS AGO
Hello
This is very nice tutorial.But I want to know if i want to overlay map more than 1 location.then what i have to do.can i write
My code is
location = new GeoPoint(230583152,725690172);
location1 = new GeoPoint(230395677,725660045);
HelloItemtizedOverlay overlay1 = new HelloItemtizedOverlay(drawable);
OverlayItem item = new OverlayItem(location,"", "");
overlay1.addOverlay(item);
location1 = new GeoPoint(230395677,725660045);
HelloItemtizedOverlay overlay1 = new HelloItemtizedOverlay(drawable);
OverlayItem item = new OverlayItem(location,"", "");
overlay1.addOverlay(item);
location1 = new GeoPoint(230395677,725660045);
OverlayItem item2 = new OverlayItem(location1,"", "");
overlay1.addOverlay(item2);
mapView.getOverlays().add(overlay1);
MapOverlay mapOverlay = new MapOverlay();
OverlayItem item2 = new OverlayItem(location1,"", "");
overlay1.addOverlay(item2);
mapView.getOverlays().add(overlay1);
MapOverlay mapOverlay = new MapOverlay();
MapOverlay mapOverlay1 = new MapOverlay();
List listOfOverlays = mapView.getOverlays();
listOfOverlays.clear();
listOfOverlays.add(mapOverlay);
List listOfOverlays = mapView.getOverlays();
listOfOverlays.clear();
listOfOverlays.add(mapOverlay);
and in MapOverlay class
mapView.getProjection().toPixels(location, screenPts);
mapView.getProjection().toPixels(location1, screenPts);
But i got only one overlay on the map.
can u help me. to display more than one overlay on google map.write some code line.thanks.Plz Reply Soon
POSTED BY DHRUVJOSHI 4 YEARS AGO
DhruvJoshi wrote:
HelloThis is very nice tutorial.But I want to know if i want to overlay map more than 1 location.then what i have to do.can i writeMy code islocation = new GeoPoint(230583152,725690172);
location1 = new GeoPoint(230395677,725660045);
HelloItemtizedOverlay overlay1 = new HelloItemtizedOverlay(drawable);
OverlayItem item = new OverlayItem(location,"", "");
overlay1.addOverlay(item);location1 = new GeoPoint(230395677,725660045);
OverlayItem item2 = new OverlayItem(location1,"", "");
overlay1.addOverlay(item2);
mapView.getOverlays().add(overlay1);
MapOverlay mapOverlay = new MapOverlay();MapOverlay mapOverlay1 = new MapOverlay();
List listOfOverlays = mapView.getOverlays();
listOfOverlays.clear();
listOfOverlays.add(mapOverlay);and in MapOverlay classmapView.getProjection().toPixels(location, screenPts);mapView.getProjection().toPixels(location1, screenPts);But i got only one overlay on the map.can u help me. to display more than one overlay on google map.write some code line.thanks.Plz Reply Soon
POSTED BY STELIOSCHAR 4 YEARS AGO
Hello,
Great tutorial...!!
Is there any way to draw a bubble that contains some information about the geotag??
POSTED BY FMLDEV 4 YEARS AGO
Awesome Tutorial! I've read 4 separate books on Android Development, this is by far the easiest to follow.
POSTED BY AHMED.NIYAS 4 YEARS AGO
Hi,
Recently i tried the same in android 2.2 SDK with google api version 8. But i m also facing the same problem, map is not displaying only grid lines are coming.
I tried opening maps through interner browser in that case it is working fine but when i tried with inbuilt map apps or my own app it is not displaying map.
anyone who resolved the same problem, please reply ASAP. Thankss in Advance
Recently i tried the same in android 2.2 SDK with google api version 8. But i m also facing the same problem, map is not displaying only grid lines are coming.
I tried opening maps through interner browser in that case it is working fine but when i tried with inbuilt map apps or my own app it is not displaying map.
anyone who resolved the same problem, please reply ASAP. Thankss in Advance
POSTED BY ZINGAR 4 YEARS AGO
hello Ahmed, i was having the same problem you have and i had tried everything.
turns out it was my mistake :P
i wasnt generating the API correctly, i had a typing error in the fingerprint and that made a invalid API key. once i figured that out i created a new API with the correct fingerprint and it worked!
turns out it was my mistake :P
i wasnt generating the API correctly, i had a typing error in the fingerprint and that made a invalid API key. once i figured that out i created a new API with the correct fingerprint and it worked!
good luck
POSTED BY DISHANF 4 YEARS AGO
Great tutorial! Thank You Mr Lee!
POSTED BY AHMED.NIYAS 4 YEARS AGO
Hi ZINGAR,
Thanks for the quick reply and Mr.Lee for a fantastic article.
Actually i was using proxy for SDk.Hence it was not working.
If i connect my sdk directly it is working fine.
Actually i was using proxy for SDk.Hence it was not working.
If i connect my sdk directly it is working fine.
Also for ppl who are facing same problem in SDK connected with proxy servers can try using your android phone(build ur app in debug mode using same procedures mentioned above) and im able to see the maps.
POSTED BY NEWBEE 4 YEARS AGO
Mr.Lee
The code for Geo coding is not working.I am not getting the address of a location that i had just touched.
please check once & send the correct code for Geo coding.
please check once & send the correct code for Geo coding.
thanks in advance.
POSTED BY AATUL.PALIWAL 4 YEARS AGO
Hi;
I have developed the map application from the tutorial and it has build successfully. Now my problem is that when i am going to deploy the application into real device, its showing me the message: Application Not Installed
I have developed the map application from the tutorial and it has build successfully. Now my problem is that when i am going to deploy the application into real device, its showing me the message: Application Not Installed
please help me.
Thanks in advance.
POSTED BY SAFADI909 4 YEARS AGO
hi, i had this problem with using maps in android
i had attached maps.jar.
just check if u have another maps.jar then this jar which is loaded with google API.
POSTED BY MR_SPS 4 YEARS AGO
Hello weimenglee,
Thanks for the nice tutorial. It's really great. I am using your code in my project.
Now I have issue, when we do zoomIn/zoomOut that time location of Markers is not showing on place but when we stop zoomIn/zoomOut than it's show on current place.
I just want th change marker position with zoom [map controller on zoomIn and zoomOut]. Can you please give me an idea.
waiting for your responce.
POSTED BY MR_SPS 4 YEARS AGO
Hello ,
Can you please help me, I have put me code here..
The issue is, when we do zoomIn/zoomOut on map I want the pin position should not change. At any point of time the position of marker can't change it's location.
Here is my code:-
public class MapsActivity extends MapActivity
{
MapView mapView;
MapController mc;
GeoPoint p;
{
MapView mapView;
MapController mc;
GeoPoint p;
class MapOverlay extends com.google.android.maps.Overlay
{
@Override
public boolean draw(Canvas canvas, MapView mapView,
boolean shadow, long when)
{
super.draw(canvas, mapView, shadow);
{
@Override
public boolean draw(Canvas canvas, MapView mapView,
boolean shadow, long when)
{
super.draw(canvas, mapView, shadow);
//---translate the GeoPoint to screen pixels---
Point screenPts = new Point();
mapView.getProjection().toPixels(p, screenPts);
//mapView.getProjection().toPixels(p, screenPts);
//---add the marker---
Bitmap bmp = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(
getResources(), R.drawable.pin);
canvas.drawBitmap(bmp, screenPts.x, screenPts.y-50, null);
return true;
}
Point screenPts = new Point();
mapView.getProjection().toPixels(p, screenPts);
//mapView.getProjection().toPixels(p, screenPts);
//---add the marker---
Bitmap bmp = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(
getResources(), R.drawable.pin);
canvas.drawBitmap(bmp, screenPts.x, screenPts.y-50, null);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, MapView mapView) {
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, MapView mapView) {
if (event.getAction() == 1) {
p = mapView.getProjection().fromPixels((int) event.getX(), (int) event.getY());
mc.animateTo(p);
//listOfOverlays.add(this);
return true;
} else{
//this.draw(this.toString(), mapView,this.SHADOW_X_SKEW, this.SHADOW_Y_SCALE);
return false;
}
p = mapView.getProjection().fromPixels((int) event.getX(), (int) event.getY());
mc.animateTo(p);
//listOfOverlays.add(this);
return true;
} else{
//this.draw(this.toString(), mapView,this.SHADOW_X_SKEW, this.SHADOW_Y_SCALE);
return false;
}
}
}
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
}
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
mapView = (MapView) findViewById(R.id.mapView);
LinearLayout zoomLayout = (LinearLayout)findViewById(R.id.zoom);
View zoomView = mapView.getZoomControls();
LinearLayout zoomLayout = (LinearLayout)findViewById(R.id.zoom);
View zoomView = mapView.getZoomControls();
zoomLayout.addView(zoomView,
new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));
mapView.displayZoomControls(true);
new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));
mapView.displayZoomControls(true);
mc = mapView.getController();
String coordinates[] = {"1.352566007", "103.78921587"};
double lat = Double.parseDouble(coordinates[0]);
double lng = Double.parseDouble(coordinates[1]);
String coordinates[] = {"1.352566007", "103.78921587"};
double lat = Double.parseDouble(coordinates[0]);
double lng = Double.parseDouble(coordinates[1]);
p = new GeoPoint(
(int) (lat * 1E6),
(int) (lng * 1E6));
(int) (lat * 1E6),
(int) (lng * 1E6));
mc.animateTo(p);
mc.setZoom(17);
mc.setZoom(17);
//---Add a location marker---
MapOverlay mapOverlay = new MapOverlay();
List listOfOverlays = mapView.getOverlays();
listOfOverlays.clear();
listOfOverlays.add(mapOverlay);
MapOverlay mapOverlay = new MapOverlay();
List listOfOverlays = mapView.getOverlays();
listOfOverlays.clear();
listOfOverlays.add(mapOverlay);
mapView.invalidate();
}
}
@Override
protected boolean isRouteDisplayed() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
}
protected boolean isRouteDisplayed() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
}
POSTED BY MAALI 4 YEARS AGO
Hej Wei-Meng
I tried this using Eclipse.
For some reason Eclipse does not read the "import com.google.android.maps" liberaries !!
For some reason Eclipse does not read the "import com.google.android.maps" liberaries !!
What do I do wrong?
BR
Maali
Maali
POSTED BY DIDACGIL9 4 YEARS AGO
Once applications like this one are done, how is it possible to deploy in mobile phones that do not contain the Google APIs? Such as the HTC Hero.
It complains (even the logcat says nothing) about a missing com.google.android.maps library.
It complains (even the logcat says nothing) about a missing com.google.android.maps library.
POSTED BY ASSEM.MOHSEN 4 YEARS AGO
to BR Maali
change your file AndroidManifest.xml like this:
POSTED BY KHAN 4 YEARS AGO
Thanks Mr. Lee for the wonderful tutorial...expect more tutorial from you on maps and location based services for android platform..a bit more explanation of the codes will be extremely useful..
POSTED BY DAVIDIZ 4 YEARS AGO
Thank you the tutorial is very well written. I do have one problem with the reversed geocode example. As far as I can determine the Try returns an exception relating to not connecting to google. My maps work so I know I have the correct apikey and permissions.
Is there something else I need from google to access the Geocode?
Is there something else I need from google to access the Geocode?
I think this is the last messages on the log:
02-11 15:59:12.848: WARN/InputReader(67): Touch device did not report support for X or Y axis!
02-11 15:59:24.678: DEBUG/SntpClient(67): request time failed: java.net.SocketException: Address family not supported by protocol
02-11 15:59:12.848: WARN/InputReader(67): Touch device did not report support for X or Y axis!
02-11 15:59:24.678: DEBUG/SntpClient(67): request time failed: java.net.SocketException: Address family not supported by protocol
These are my imports:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Locale;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Point;
import android.location.Address;
import android.location.Geocoder;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.Toast;
import com.google.android.maps.GeoPoint;
import com.google.android.maps.MapActivity;
import com.google.android.maps.MapController;
import com.google.android.maps.MapView;
import com.google.android.maps.MapView.LayoutParams;
import com.google.android.maps.Overlay;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Point;
import android.location.Address;
import android.location.Geocoder;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.Toast;
import com.google.android.maps.GeoPoint;
import com.google.android.maps.MapActivity;
import com.google.android.maps.MapController;
import com.google.android.maps.MapView;
import com.google.android.maps.MapView.LayoutParams;
import com.google.android.maps.Overlay;
Here is my code: (there are no errors)
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, MapView mapView)
{
//---when user lifts his finger---
if (event.getAction() == 1) {
GeoPoint p = mapView.getProjection().fromPixels(
(int) event.getX(),
(int) event.getY());
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, MapView mapView)
{
//---when user lifts his finger---
if (event.getAction() == 1) {
GeoPoint p = mapView.getProjection().fromPixels(
(int) event.getX(),
(int) event.getY());
Geocoder geoCoder = new Geocoder(
getBaseContext(), Locale.getDefault());
try {
List addresses = geoCoder.getFromLocation(
p.getLatitudeE6() / 1E6,
p.getLongitudeE6() / 1E6, 1);
getBaseContext(), Locale.getDefault());
try {
List addresses = geoCoder.getFromLocation(
p.getLatitudeE6() / 1E6,
p.getLongitudeE6() / 1E6, 1);
String add = "";
if (addresses.size() > 0)
{
for (int i=0; i i++)
add += addresses.get(0).getAddressLine(i) + "\n";
}
Toast.makeText(getBaseContext(), add, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if (addresses.size() > 0)
{
for (int i=0; i
add += addresses.get(0).getAddressLine(i) + "\n";
}
Toast.makeText(getBaseContext(), add, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
}
POSTED BY NISCHAL 4 YEARS AGO
hi ,
i am successful in displaying google map .
now i want to add "search" option to it .i.e the user can give a place name as input and our map should display that respective position
how can i do this ?
can anyone plz do guide me?
nischal










POSTED BY FEATUREBLEND 6 YEARS AGO
POSTED BY ARNOUF 6 YEARS AGO
MapView.setBuiltInZoomControls(true)
POSTED BY NEHA 6 YEARS AGO
D/dalvikvm( 609): GC freed 2803 objects / 171408 bytes in 214ms I/Process ( 751): Sending signal. PID: 751 SIG: 9 I/ActivityManager( 567): Process edu.blah (pid 751) has died. W/InputManagerService( 567): Window already focused, ignoring focus gain of: com.android.internal.view.IInputMethodClient$Stub$Proxy@43740c48 I/ActivityManager( 567): Starting activity: Intent { action=android.intent.action.MAIN categories={android.intent.category.LAUNCHER} flags=0x10200000 comp={edu.blah/edu.blah.MyMapsActivity} } I/ActivityManager( 567): Start proc edu.cmu.android.bmo for activity edu.cmu.android.bmo/.MyMapsActivity: pid=758 uid=10020 gids={} I/jdwp ( 758): received file descriptor 20 from ADB E/jdwp ( 758): Failed sending req to debugger: Broken pipe (-1 of 27) E/jdwp ( 758): Failed sending reply to debugger: Broken pipe I/dalvikvm( 758): Debugger has detached; object registry had 2 entries W/dalvikvm( 758): Class resolved by unexpected DEX: Ledu/blah/MyMapsActivity;(0x43734570):0x18fbc0 ref [Lcom/google/android/maps/MapActivi ty;] Lcom/google/android/maps/MapActivity;(0x43734570):0x185c58 W/dalvikvm( 758): Unable to resolve superclass of Ledu/cmu/android/bmo/MyMapsActivity; (40) W/dalvikvm( 758): Link of class 'Ledu/blah/MyMapsActivity;' failed D/AndroidRuntime( 758): Shutting down VM W/dalvikvm( 758): threadid=3: thread exiting with uncaught exception (group=0x4000fe70) E/AndroidRuntime( 758): Uncaught handler: thread main exiting due to uncaught exception E/AndroidRuntime( 758): java.lang.IllegalAccessError: cross-loader access from pre-verified class E/AndroidRuntime( 758): at dalvik.system.DexFile.defineClass(Native Method) E/AndroidRuntime( 758): at dalvik.system.DexFile.loadClass(DexFile.java:193) E/AndroidRuntime( 758): at dalvik.system.PathClassLoader.findClass(PathClassLoader.java:203) E/AndroidRuntime( 758): at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:573) E/AndroidRuntime( 758): at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:532) E/AndroidRuntime( 758): at android.app.Instrumentation.newActivity(Instrumentation.java:1097) E/AndroidRuntime( 758): at android.app.ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2186) E/AndroidRuntime( 758): at android.app.ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2284) E/AndroidRuntime( 758): at android.app.ActivityThread.access$1800(ActivityThread.java:112) E/AndroidRuntime( 758): at android.app.ActivityThread$H.handleMessage(ActivityThread.java:1692) E/AndroidRuntime( 758): at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:99) E/AndroidRuntime( 758): at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:123) E/AndroidRuntime( 758): at android.app.ActivityThread.main(ActivityThread.java:3948) E/AndroidRuntime( 758): at java.lang.reflect.Method.invokeNative(Native Method) E/AndroidRuntime( 758): at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:521) E/AndroidRuntime( 758): at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(ZygoteInit.java:782) E/AndroidRuntime( 758): at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:540) E/AndroidRuntime( 758): at dalvik.system.NativeStart.main(Native Method) I/Process ( 567): Sending signal. PID: 758 SIG: 3 I/dalvikvm( 758): threadid=7: reacting to signal 3 I/dalvikvm( 758): Wrote stack trace to '/data/anr/traces.txt' I/jdwp ( 758): received file descriptor 26 from ADB W/ActivityManager( 567): Launch timeout has expired, giving up wake lock! W/ActivityManager( 567): Activity idle timeout for HistoryRecord{43735178 {edu.blah/edu.blah.MyMapsActivity}} D/dalvikvm( 609): GC freed 1862 objects / 102376 bytes in 202ms I/Process ( 758): Sending signal. PID: 758 SIG: 9 I/ActivityManager( 567): Process edu.blah (pid 758) has died.POSTED BY KATALYTE 6 YEARS AGO
I try to develope this tutorial but the application load but i cannot see the map (all i see is a grid). I have follow the all intructions with permission and apikey but still see nothing!
POSTED BY NAGA_VEJJU 6 YEARS AGO
Nagesh
POSTED BY KATALYTE 6 YEARS AGO
send again
POSTED BY JAIMIK_DS 6 YEARS AGO
06-23 03:04:07.314: WARN/SystemClock(90): Unable to set rtc to 1245751447: Invalid argument
06-23 03:04:07.984: DEBUG/ActivityManager(51): Uninstalling process net.learn2develop.GoogleMaps
06-23 03:04:07.984: INFO/ActivityManager(51): Starting activity: Intent { flags=0x10000000 comp={net.learn2develop.GoogleMaps/net.learn2develop.GoogleMaps.MapsActivity} }
06-23 03:04:08.006: WARN/ActivityManager(51): Permission Denial: starting Intent { flags=0x10000000 comp={net.learn2develop.GoogleMaps/net.learn2develop.GoogleMaps.MapsActivity} } from null (pid=-1, uid=-1) requires android.permission.INTERNET
06-23 03:04:08.016: DEBUG/AndroidRuntime(150): Shutting down VM
06-23 03:04:08.016: WARN/dalvikvm(150): threadid=3: thread exiting with uncaught exception (group=0x40010e28)
06-23 03:04:08.016: ERROR/AndroidRuntime(150): Uncaught handler: thread main exiting due to uncaught exception
06-23 03:04:08.016: ERROR/AndroidRuntime(150): *** EXCEPTION IN SYSTEM PROCESS. System will crash.
06-23 03:04:08.065: ERROR/AndroidRuntime(150): java.lang.SecurityException: Permission Denial: starting Intent { flags=0x10000000 comp={net.learn2develop.GoogleMaps/net.learn2develop.GoogleMaps.MapsActivity} } from null (pid=-1, uid=-1) requires android.permission.INTERNET
06-23 03:04:08.065: ERROR/AndroidRuntime(150): at android.os.Parcel.readException(Parcel.java:1234)
06-23 03:04:08.065: ERROR/AndroidRuntime(150): at android.os.Parcel.readException(Parcel.java:1222)
06-23 03:04:08.065: ERROR/AndroidRuntime(150): at android.app.ActivityManagerProxy.startActivity(ActivityManagerNative.java:998)
06-23 03:04:08.065: ERROR/AndroidRuntime(150): at com.android.commands.am.Am.runStart(Am.java:197)
06-23 03:04:08.065: ERROR/AndroidRuntime(150): at com.android.commands.am.Am.run(Am.java:73)
06-23 03:04:08.065: ERROR/AndroidRuntime(150): at com.android.commands.am.Am.main(Am.java:51)
06-23 03:04:08.065: ERROR/AndroidRuntime(150): at com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit.finishInit(Native Method)
06-23 03:04:08.065: ERROR/AndroidRuntime(150): at com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit.main(RuntimeInit.java:186)
06-23 03:04:08.065: ERROR/AndroidRuntime(150): at dalvik.system.NativeStart.main(Native Method)
06-23 03:04:08.075: ERROR/JavaBinder(150): Unknown binder error code. 0xfffffff7
06-23 03:04:08.094: ERROR/AndroidRuntime(150): Crash logging skipped, no checkin service
POSTED BY KATALYTE 6 YEARS AGO
POSTED BY AGARWALSONAL 6 YEARS AGO
I am successfully able to fetch the address of the street using the Geocoder function by providing the longitude and latitude of the street point of view.
With Regards,
Sonal
POSTED BY ARAMSVIVEK 6 YEARS AGO
POSTED BY LIFEF 6 YEARS AGO
POSTED BY CAWA 5 YEARS AGO
but I have a little more question for you: can I change the pin position just by touching the screen?
class MapOverlay extends com.google.android.maps.Overlay { @Override public boolean draw(Canvas canvas, MapView mapView, boolean shadow, long when) { super.draw(canvas, mapView, shadow); Point screenPts = new Point(); mapView.getProjection().toPixels(p, screenPts); Bitmap bmp = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.pin); canvas.drawBitmap(bmp, screenPts.x, screenPts.y-48, null); return true; } @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, MapView mapView) { if (event.getAction() == 1) { GeoPoint p = mapView.getProjection().fromPixels((int) event.getX(), (int) event.getY()); mc.animateTo(p); MapOverlay mapOverlay = new MapOverlay(); listOfOverlays = mapView.getOverlays(); listOfOverlays.clear(); listOfOverlays.add(mapOverlay); return true; } else return false; } }thanks!
POSTED BY ZXY861114 5 YEARS AGO
The code can achieve your aim.
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, MapView mapView) {
if (event.getAction() == 1) {
p = mapView.getProjection().fromPixels((int) event.getX(), (int) event.getY());
mc.animateTo(p);
return true;
} else return false;
}
POSTED BY SING522 5 YEARS AGO
^_^
POSTED BY MSALMANQ 5 YEARS AGO
Salman
POSTED BY JHM15217 5 YEARS AGO
POSTED BY JHM15217 5 YEARS AGO
http://maps.google.com/maps?saddr=1788+Oak+Creek+Dr+94304+to:1600+Amphitheatre+Parkway+94043
to the browser gets me directions, but feeding it as part of an Android intent causes the maps app enter direction-finding mode but it misses the "to:" part.
POSTED BY AAMIRYASEEN 5 YEARS AGO
I am having two problem when implementing my Android Map based application, can you help?
1- How can I zoom map, so that all the added overlays are visible?
2- how can I show information in bubble, when use select one of the added overlay (in this case icon).?
Aamir
POSTED BY MRSIMONS 5 YEARS AGO
POSTED BY RUADHAN 5 YEARS AGO
debug.keystorefile located in the default location mentioned in the article, look in theC:\Documents and Settings\\.android folderEditor, mobiForge
POSTED BY VT515 5 YEARS AGO
James
POSTED BY SAM82T 5 YEARS AGO
I have followed all the new instructions preoperly but I am not able to see the Map, only the grids are visible.
Any solution fo this problem
POSTED BY RD42 5 YEARS AGO
I'm stumped. I'm using Eclipse and I copied and pasted the AndroidManifest directly into mine and it won't compile because the